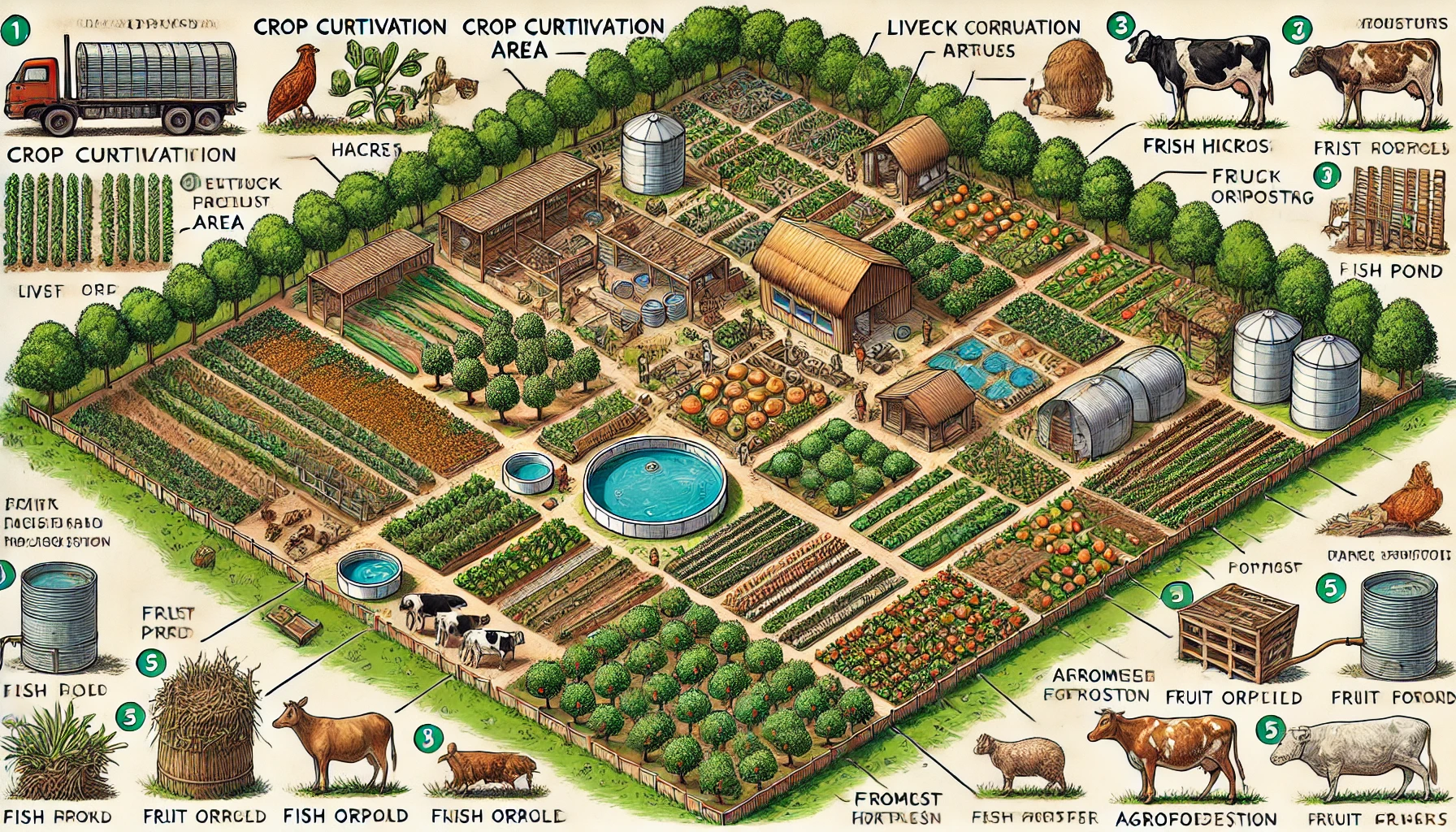
To establish a sustainable integrated farming system combining crop production, livestock, aquaculture, and horticulture to maximize productivity, ensure environmental sustainability, and generate multiple income streams.
1. Project Phases and Timeline Overview (12 Months Plan)
| Phase | Activities | Duration | Completion Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Planning & Preparation | Land preparation, sourcing materials, permits | 1 month | Month 1 |
| Phase 2: Infrastructure Development | Construct livestock shed, fish pond, vermicompost unit | 2 months | Month 2-3 |
| Phase 3: Planting & Livestock Setup | Plant crops and fruit trees, introduce livestock & fish | 2 months | Month 4-5 |
| Phase 4: Operations & Maintenance | Irrigation, feeding, monitoring health, composting | Ongoing (Daily/Weekly) | Month 6 onward |
| Phase 5: Harvesting & Sales | Crop, milk, fish, and compost harvesting | Ongoing | Month 6-12 |
| Phase 6: Expansion & Optimization | Evaluate, reinvest profits, diversify crops/livestock | Ongoing | Month 12 and beyond |
2. Detailed Activity Breakdown by Phase
Phase 1: Planning & Preparation (Month 1)
- Land Survey: Soil testing, water source identification.
- Budgeting & Sourcing: Seeds, livestock, fish seed, equipment, fertilizers.
- Permits & Approvals: Local government permits for livestock and aquaculture.
- Training & Consultation: Attend workshops or consult experts.
Estimated Cost: INR 20,000 – 30,000
Phase 2: Infrastructure Development (Month 2-3)
- Livestock Shed Construction (0.1 ha): For 2-3 cows/goats, 50-100 poultry.
- Fish Pond Excavation (0.1 ha): Design a pond with a drainage and aeration system.
- Vermicomposting Unit (0.05 ha): Construct compost pits.
- Irrigation System: Install drip or sprinkler irrigation for efficient water use.
- Storage Facility: Build a small shed for tools, feed, and storage.
Estimated Cost: INR 1,50,000 – 2,00,000
Phase 3: Planting & Livestock Setup (Month 4-5)
- Crop Cultivation (0.5 ha): Plant cereals (e.g., maize, wheat) and vegetables (e.g., tomatoes, okra).
- Fruit Tree Plantation (0.15 ha): Plant mango, papaya, or banana.
- Livestock Procurement: Purchase 2-3 cows/goats and 50-100 poultry chicks.
- Fish Stocking: Introduce fish seed into the pond (e.g., catfish, tilapia).
Estimated Cost: INR 1,00,000 – 1,50,000
Phase 4: Operations & Maintenance (Month 6 Onward)
- Daily Tasks: Watering crops, feeding livestock, maintaining ponds, monitoring health.
- Waste Management: Collect livestock waste for composting, and recycle fish pond water for irrigation.
- Monitoring Growth: Inspect crops, livestock health, and fish growth regularly.
Estimated Monthly Cost: INR 10,000 – 15,000
Phase 5: Harvesting & Sales (Months 6-12)
Crop Harvest: 2-3 harvests per year, depending on the crop cycle.
- Milk Production: Daily or twice-daily milk collection.
- Fish Harvest: Harvest fish after 6 months.
- Compost Sales: Sell vermicompost to local farmers or nurseries.
Estimated Revenue (Annual):
- Crops: INR 1,50,000 – 2,00,000
- Livestock (Milk, Meat, Eggs): INR 1,50,000 – 2,00,000
- Fish: INR 50,000 – 1,00,000
- Vermicompost: INR 30,000 – 50,000
Total Annual Revenue Estimate: INR 4,30,000 – 6,20,000
Phase 6: Expansion & Optimization (Month 12 Onward)
Reinvestment: Use profits to expand livestock, add new crops, or set up renewable energy (solar/biogas).
- Diversification: Introduce value-added products like dairy products (ghee, butter) or organic vegetables.
- Technology Upgrades: Invest in mechanization (e.g., tillers, water pumps) or automation (smart irrigation).
3. Financial Summary
| Component | Cost Estimate (INR) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Land Preparation | 20,000 – 30,000 | Plowing, leveling |
| Infrastructure Setup | 1,50,000 – 2,00,000 | Shed, fish pond, compost unit |
| Crop & Livestock Inputs | 1,00,000 – 1,50,000 | Seeds, fertilizers, livestock, fish seed |
| Miscellaneous Expenses | 30,000 | Fencing, irrigation, tool storage |
| Total Initial Investment | 3,30,000 – 4,50,000 |
4. Risks and Mitigation Strategies:
- Weather Risks: Install rainwater harvesting and drought-resistant crops.
- Market Fluctuations: Diversify crops and livestock to spread risk.
- Pest and Disease: Use integrated pest management (IPM) and maintain livestock health protocols.
5. Conclusion:
This business plan focuses on sustainability, efficient resource utilization, and diversification. With careful management, integrated farming on 1 hectare can yield both financial and ecological benefits.
Financial and Business expert having 30+ Years of vast experience in running successful businesses and managing finance.





