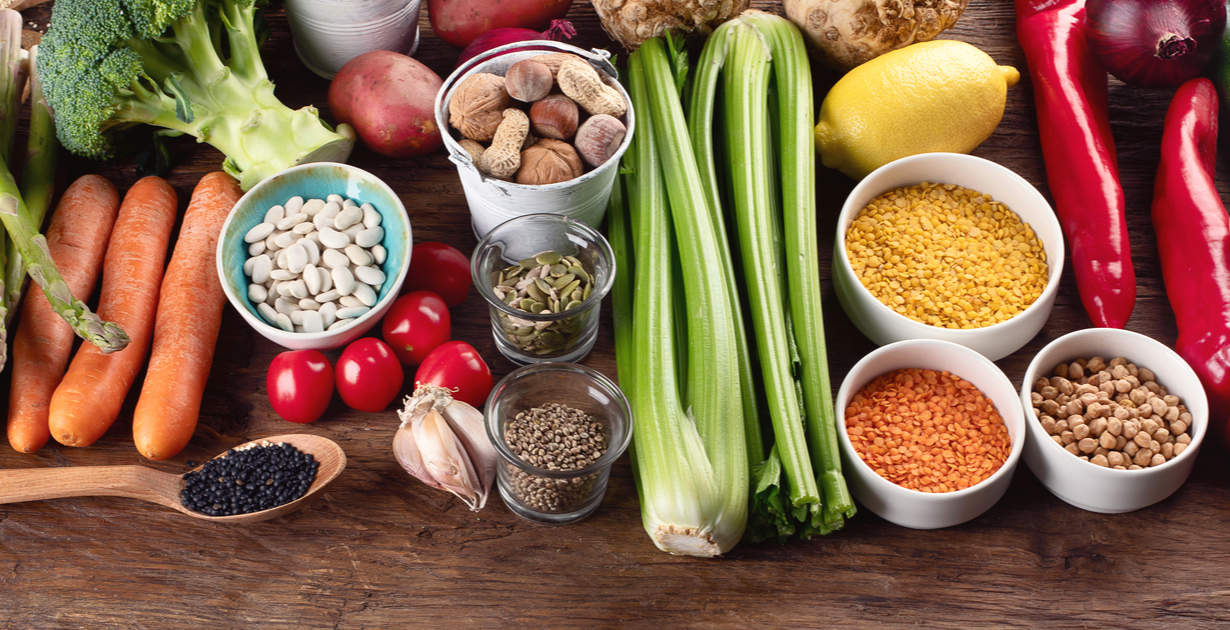
Essential nutrients are crucial in supporting a person’s reproduction, good health, and growth. These essential nutrients are divided into two categories: micronutrients and macronutrients including fatty acids and amino acids.
A nutrient is anything that provides nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life. Many nutrients are good for us, but there are a few that we need to be particularly mindful of to incorporate into our diets.
Keep reading for more information about where to find these nutrients, and why a person needs them.
Water
Keeping hydrated is really important. Water is absolutely essential for survival, especially as it makes up 60% of the human adult body. A few days without water can lead to serious illness and even death. Our body relies on water. It is critical for waste removal and temperature regulation and is an essential element of every cell.
To remain hydrated, drink water throughout the day, and eat foods with high water content – fruits and vegetables in particular. Keep drinks, like coffee and nasty soft drinks which dehydrate you to a minimum.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates, or carbs, often get a bad rap as fattening, with many no-carb diets emerging in recent years. Like any nutrient, consuming carbs is all about balance. In reality, carbs are essential for proper body function. Carbs are broken down into glucose, which is your brain and body’s main fuel.
Carbs also ensure your body is not breaking down proteins to gain energy, preventing the loss of muscle mass. Complex carbohydrates take longer to break down and keep you fuller for longer, meaning you cut down on unhealthy snacking. Whole grains, vegetables, and fruits are all examples of healthy complex carbohydrates.
Protein-Amino acids
Protein is critical for good health. Protein is essential in forming muscles to create new enzymes and hormones. Proteins are comprised of small building blocks called amino acids. They are the building blocks of cells, which turn over quicker and regenerate more slowly as a person ages. Ensuring these vital building blocks are there helps enhance optimal ageing at the time of your life when it becomes more important to support your nutritional intake and make up for any deficiencies. There are 20 amino acids in total, but the nine essential amino acids are:
- Histidine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Lysine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Valine
Proteins carry out a variety of functions including:
ensuring the growth and development of muscles, bones, hair, and skin
forming antibodies, hormones, and other essential substances
serving as a fuel source for cells and tissues when needed
A person can take in proteins through their diet. The following foods are good sources of protein:
- red meats (limit their use and choose lean cuts)
- poultry, including chicken and turkey
- fish and other seafood
- beans and legumes
- eggs
- dairy products
- soy
- nuts
- some grains, including quinoa
Animal proteins provide all essential amino acids, while plant proteins may be lacking several of these essential elements. To ensure you’re getting all essential amino acids, include a variety of proteins in your diet, such as meat, eggs, dairy, nuts, and beans. Where you do eat meat, try to eat only lean meat.
Fat
Another oft-targeted nutrient, dietary fat has earned a bad reputation because of its association with body fat. A multitude of diets have sprung up condemning all fat, but the reality is much more nuanced. Fat is an essential nutrient that boosts the absorption of vitamins and helps protect organs.
Healthful fats help with the following functions:
- cell growth
- blood clotting
- building new cells
- reducing the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes
- muscle movement
- balance blood sugar
- brain functioning
- mineral and vitamin absorption
- hormone production
- immune function
Some types of fats are undoubtedly bad. Trans fats, found in processed and baked foods, increase the risk of heart disease and should be eaten very rarely, if ever. Unsaturated fats, found in natural sources, actually protect the heart and aid the prevention of heart disease. These good fats can be found in nuts, avocados and salmon.
Vitamins
A vitamin is an organic compound and an essential micronutrient that the body needs in small amounts. The essential vitamins are:
- Vitamin A is vital for skin and eye health.
- Vitamin C for bone and muscle structure and immune support.
- Vitamin D for bone growth and cardiovascular and nervous health. It is particularly critical for bone and immune health, so it’s a must-have.
- Vitamin E is a nutrient that’s important to vision, reproduction, and the health of your blood, brain and skin.
- B vitamins are important for making sure the body’s cells are functioning properly. Water soluble vitamins are:
vitamin B-1 (thiamine)
vitamin B-12 (cyanocobalamin)
vitamin B-6
vitamin B-2 (riboflavin)
vitamin B-5 (pantothenic acid)
vitamin B-3 (niacin)
vitamin B-9 (folate, folic acid)
vitamin B-7 (biotin)
Vitamins are micronutrients that offer a range of health benefits, including:
- boosting the immune system
- helping prevent or delay certain cancers, such as prostate cancer
- strengthening teeth and bones
- aiding calcium absorption
- maintaining healthy skin
- helping the body metabolize proteins and carbs
- supporting healthy blood
- aiding brain and nervous system functioning
No food provides every essential vitamin. A diverse and healthy diet is needed. If your diet is restrictive, there’s nothing wrong with taking a supplement which contains multivitamins to fill in the gaps. That said, try and get your vitamins naturally where possible. Unfortunately, though for most of us, this isn’t possible, so make sure you get them through other means.
Minerals
Minerals are another essential micronutrient, with each essential mineral fulfilling a different role. Seven essential minerals are:
- Sodium
- Iron
- Potassium
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Zinc
- Phosphorus
Major minerals help the body to do the following:
- balance water levels
- maintain healthy skin, hair, and nails
- improve bone health
Calcium is essential for bone health, muscle and nerve function, and circulation. 99 per cent of the body’s calcium is found in the bones and teeth. Calcium is found in dairy, leafy greens and fish such as sardines and salmon.
Sodium is another essential nutrient that’s gained a bad reputation. Sodium keeps nerves and muscles working correctly. Sodium should be consumed carefully. It is all about moderation. Sodium can be found naturally in nuts, vegetables, meats and legumes, but intake should be limited to around one teaspoon of salt. Processed, frozen, and canned foods with high sodium should be avoided.
In summary, while we should be putting all of these important building blocks into our body every day, unfortunately, due to diet, toxins, alcohol, pollution, poor quality food, lack of rest, etc, we often don’t give our body what it needs. Over a longer period of time, this can cause problems which can then lead to illness. It is best if we avoid this and give our body what it needs.
Financial and Business expert having 30+ Years of vast experience in running successful businesses and managing finance.