
Different types of farming systems
The process of growing crops and rearing animals for food and raw materials like vegetables, fruits, milk, fibre, meat etc. is called farming. Under the broad spectrum of agriculture, farming is considered a small category which involves production of flowers, fruits, bio-fuels, drugs, fibres, nursery plants, manure and leather. Different types of farming systems practiced in India are:
- Subsistence farming
- Shifting agriculture
- Plantation agriculture
- Intensive farming
- Dry agriculture
- Mixed farming
- Crop rotation
- Sedentary farming
- Terrace cultivation (hilly area farming)
Importance of agriculture
Sometimes it is observed that agriculture is not just production of materials, but it also involves promotion, processing and distribution of produced materials. Agriculture is important because of the following reasons:
- Source of livelihood.
- Contributes to the national revenue.
- Serves food for both human beings and animals.
- Has the great significance due to export of various items.
- Creates surplus material in the market.
- Source of raw material
- Creates employment opportunities.
- Helps with economic development.
- Guarantees food security.
 Branches of agriculture
Branches of agriculture
The different branches of agriculture are:
- Horticulture
- Aquaculture
- Dairy farming
- Organic farming
- Poultry
- Sericulture
- Vermiculite
- Market gardening
If the broad definition of agriculture is taken into consideration then it could also involve branches, like
- Sseed technology
- Nematology
- Plant breeding
- Genetics
- Soil science
- Agronomy
 Procedure of Growing Crops
Procedure of Growing Crops
Farmers need to understand the following points to have a successful farming business. The basic knowledge of cultivation along with the required resources helps farmers to grow their crops.
- Local growing conditions
- Soil requirements
- Crop compatibility
The general requirements are soil/land, nutrients/fertilizers , air, water, sunlight and of course farm equipment. Apart from all these, farmers need investment (money) for getting seeds, manure, irrigation facilities, labour and other farm materials to begin with. Using all these resources at the right time for the right crop, farmers cultivate or grow plants and produce food.
 Methods of farming
Methods of farming
Some methods for sustainable farming are:
- Crop rotation and diversity
- Growing cover crops
- Reducing tillage
- Considering integrated pest management
- Adopting integrated farming (livestock and crops)
- Following agro-forestry practices
- Managing the landscapes and the farming systems
 Ley farming
Ley farming
Farming is very difficult in dry lands because of water scarcity and lack of soil fertility, so a method of farming was introduced to restore the fertility of the soil and was known as ley farming. In this method of farming, grasses were grown in rotation with food grains to boost the nutrient level of the soil. It acts as an insurance against crop failures due to drought conditions.
Contour farming
The process of planting across a slope following its elevation contour lines. In this practice the ruts made by the plough are perpendicular to the slope rather than being parallel. Plants break the flow of water and prevent soil erosion, thereby making contour farming a sustainable way of farming.
 Hedgerow inter-cropping
Hedgerow inter-cropping
The practice of growing annual crops in between the rows of trees as an alternate method of fallow system is termed as hedgerow inter-cropping. The combination of trees and crops complement each other rather than competing. The trees create a favourable micro-climate for the crops to survive by shielding them from drying winds.
 Crop rotation
Crop rotation
The method of growing different types of crops in the same area during sequenced seasons is called crop rotation. This is done mainly to prevent soil erosion due to mono-cropping. It is very clearly known that growing only a certain variety of crops in the same area depletes the region of one particular kind of nutrient, therefore, to keep or maintain the balance of nutrients in the soil a different crop is grown for a certain duration or season to help restore the imbalance.
Advantages of crop rotation
The general pattern of following a seasonal calendar for planting crops is now being termed as crop rotation and the possible advantages of this technique as:
- Improves soil fertility by increasing the nutrient and organic content in the soil.
- Provides proper nourishment and increases crop yield.
- Replenishes nutrients into the soil.
- Reduces soil erosion.
- Reduces the concentration of pests and diseases.
- Decreases the impact of weeds.
- Improves the physical structure of the soil.
- Reduces the pollution caused by fertilizers.
 Duties of a farmer
Duties of a farmer
A farmer has to carry out different tasks throughout the crop life cycle and has to undertake a different set of duties if he is livestock. Most important activities of a farmer are
- Cleaning
- Tractor driving
- Ploughing
- Planting
- Managing livestock
- Feeding livestock
- Harvesting
- Marketing of produce
- Carrying out intercultural activities, fertilizing, irrigating, farm maintenance etc.
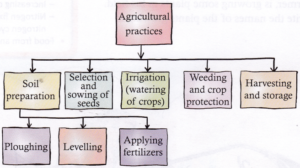 Steps of agriculture Process
Steps of agriculture Process
The entire process of farming involves a series of steps called as crop lifecycle, which starts at crop selection and ends at harvesting. The steps for growing crops are:
- Crop selection
- Preparing the land
- Selecting the seeds
- Sowing
- Manure and fertilizer application
- Irrigation
- Intercultural activities
- Management of pest and diseases
- Harvesting
- Post harvest management
- Sale of produce
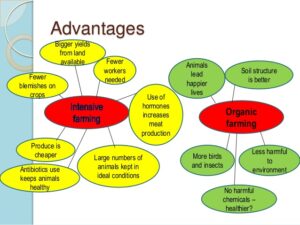 Advantages of ideal crop production
Advantages of ideal crop production
Crop production has too many benefits on different aspects of farming because of proper maintenance during the entire cycle such as:
- It restores the natural nitrogen fixing ability of the soil, improves microbial activity, balances salinity and acidity levels of the soil, prevent soil erosion etc.
- Controls the insects, pests and soil borne diseases.
- Prevents the peak requirement of water between irrigation cycles.
- Employment to the labourers.
- Regular flow of income to the farmer.
- Producing different crops maintains the nutrient efficiency of the soil.
- Diversification of crops helps the farmer maintain good financial condition.
- Regular cultivation reduces the risk of hard pan formation in the sub-soil level.
- Helps farmers understand the potential risks of cultivating certain crops like groundnuts, soybean etc.
- The produce from the farm helps the survival of the labour as well as supplies the external market.
- Availability of raising short duration crops for immediate income.
 Harrowing in agriculture
Harrowing in agriculture
Harrowing is breaking up the soil and smoothing its surface for planting crops. Generally, after the ploughing operation, the soil has a very rough and unfinished texture which is not suitable for farming. The clods or lumps of soil are broken up into a fine powder like substance and made extremely soft for planting saplings or sowing seeds. Harrowing is also done to remove weeds, but the intensity is low and is called coarser harrowing. There are machines available for harrowing like
- Disc harrows
- Tine harrows
- Spring tooth harrows
- Drag harrows
- Chain harrows
Traditional harrowing was done by draft animals, but now the equipment is being mounted on a tractor and manual labourers perform the operation.
 Soil requirement in agriculture
Soil requirement in agriculture
Soil is the first basic requirement while farming because it is the main source of nutrients to the plants. Healthy soil produces the most food. The soil is considered as a living, dynamic ecosystem that helps in converting dead, decayed matter into nutrients with the presence of microorganisms.
Agricultural or farming aims at growing crops in soil so that they consume nutrients and in turn provide it in the form of vegetables and fruits. Soil acts as a medium for the supply of nutrients and water to the plants. Once the nutrients and water are used up, it is supplemented using fertilizers and irrigation respectively.
 Land preparation for farming
Land preparation for farming
The main idea of land preparation is to get the soil or field ready for planting and this may involve activities like removal of weeds and unwanted materials like stones, recycling plant nutrients, making the soil fine in texture etc. Land preparation has to be carried out either by zero-tillage or minimum tillage so as to keep the soil disturbance levels minimum because a totally puddled soil would have a destroyed structure for cultivation. Tilling the soil can be done by ploughing, harrowing and leveling
 Planting in agriculture
Planting in agriculture
Incorporating the saplings or seeds in the main farming area after proper land preparation is called planting. It is basically of two types:
- Direct seeding
- Transplanting
 Importance of Tillage
Importance of Tillage
Tilling is deep ploughing the land almost to the depth of 8-10 inches while preparing the soil for cultivation. When the soil condition is very poor, then a large quantity of organic matter has to be incorporated into it and this can be done only by tilling the soil. Other important reasons for tilling the soil could be facilitating air circulation, decomposition, etc. Tilling can be done in many ways and is expected to have its own advantages and disadvantages.
 Land cleaning/clearing
Land cleaning/clearing
The process of removing trees, stumps, brush, stones and other unwanted substances from the farm area is called land clearing. Doing so improves the productivity of the land and provides a new land base for next crop cycle. The land clearing process also involves piling up the debris and disposing it by burning the pile. Land is cleared using clearing equipment maintained by trained operators. Piling rakes and blades are also used while cleaning.
 Factors that affect crop production
Factors that affect crop production
The crop production cycle depends on two major factors, i.e. internal and external factors. The internal factors that influence the crop growth relate to the genetic capability of the seed or variety of crop being cultivated and the desirable characteristics for proper production are:
- Excellent yielding ability
- Early maturity
- Resistance to diseases and lodging
- Tolerance to drought and pests
- Good chemical composition like oil and protein
- Tolerant to soil pH levels
- Good quality of produce or grains
- Good quality of straw
The external factors that influence the growth of the crop are mostly the environmental conditions of the region and could be subdivided into different factors like following
Climatic factors – Pecipitation, temperature, atmospheric humidity, solar radiation, wind velocity and atmospheric gases.
Edaphic factors – Soil moisture, soil air, soil temperature, mineral matter, organic matter, organisms and reactions (pH).
Biotic factors – Pants and animals.
Physiographic factors – Topography, altitude, slope/steepness, exposure to wind and light.
Socio-economic factors – Choice of crops, availability of labour, discovery of new breeding varieties and economic condition of the farmer.
 Difference between sowing and transplanting
Difference between sowing and transplanting
There are two major ways in which planting could be done are direct seeding and transplanting. Direct seeding refers to planting the seeds in the fields for growing crops, whereas transplanting refers to planting saplings or seedlings that have been grown in nurseries from seeds.
The term ‘sowing’ is used when seeds are sown directly into the prepared area or nursery pots or bags. Sowing seeds need a different soil condition and environment for proper germination. The depth of sowing and the management practices while handling seeds is considered risky. Plants grown directly from seeds have a long cultivation time period.
The term ‘transplanting’ is used when seedlings from the nursery are moved into the main farming area or final growing area. The soil conditions and environmental factors for seedlings should be prepared properly to avoid loss and root damage. Seedlings or saplings obtained from trusted nurseries can be handled easily by maintaining better farm practices.
Generally, cereal crops such as rice, corn, millets, sorghum; pulses (soybean, peanut); large seeded vegetables (squash, melons); root vegetables, leafy vegetablesare grown by direct seeding.
Small seeded vegetables like eggplant, tomato, pepper; fruit plants, ornamentalplants, coconut plant and palm plants are cultivated using transplants.
Vegetables like cabbage, mustard, lettuce etc. are generally grown in either ways: direct seeding or transplanting.
Broadcasting and transplanting
Scattering the seeds on the farm area either manually or mechanically is called broadcast seeding. This is exactly opposite or in contrast to precision seeding (planting seeds at the proper depth and place) and hydro seeding (spraying slurry of seeds, mulch and water in a uniform layer over prepared farm areas). The broadcasting method needs 10-20% extra seeds for sowing when compared to other sowing methods.
Transplanting is not associated with seeds rather it is planting of saplings or seedling onto the farm area. The seeds from which the saplings are obtained are generally sown in a nursery and grown under protected conditions.
 Need of grains dried before storage
Need of grains dried before storage
If grains that have been freshly harvested are stored without drying, then they may be spoiled due to micro-organism infestation. Drying the grains removes moisture from them so as to improve their shelf life and reduce the attack by insects, pests, bacteria and fungi. If the grains or seeds are to be used for sowing then moist grains lose the ability of germination very fast. So it is always advised to dry the seeds up to 12% before storing.
 Treatment of seeds before sowing
Treatment of seeds before sowing
Seeds are treated with chemicals prior to planting so as to protect them from microbial attacks and decay. The main aim of coating the seeds with insecticides and fungicides is to keep them safe from diseases. Chemicals are also coated over the seeds to increase the germinating ability of the seeds.
 Cover crop in farming and its benefits
Cover crop in farming and its benefits
Cover crops are also called green manure crops and are primarily used to repair the soil structure. Cover crops aid in sustainable farming and aim to improve the agro-ecosystem. Examples of cover crops are legumes (peas and beans), mustard, daikon, wheat, barleyand rye. Some exceptional benefits of cover crops are:
- Prevents soil erosion
- Improves soil structure
- Increases organic content in the soil
- Helps in suppressing weeds
- Retains moisture content
- Adds valuable nutrients
- Reduces the labour work for mulching
- Produce food just like other crops
- Helps in better biodiversity
- Attracts beneficial insects and pollinators
 Use of a combination of manures and fertilizers in fields
Use of a combination of manures and fertilizers in fields
Manure is an organic matter which has many nutrients packed into a tremendously interconnected structure (like a web). Generally, if only a required nutrient is applied as fertilizer to the plants, then there is a possible risk of it being leached away or lost due to fixation. This results in insufficient supply of nutrient to the plant, but if fertilizer is applied along with manure then it remains in the soil structure (packed in the net like structure of manure) without getting leached and is made available for the plants.
 Dibbling method
Dibbling method
Dibbling is a method of cultivation, which uses an instrument called dibbler to plant seeds into the soil. A dibbler is a pointed stick that creates hole in the ground and plants the seed or seedling into it. Dibbling is not just placing the seedlings into the hole; it is used in conjunction with another process called puddling. Puddling is planting a seedling into a small hole filled with water in the ground.
 Irrigation in agriculture
Irrigation in agriculture
Irrigation in agriculture refers to the controlled application of water through man-made systems. These systems are particularly designed to solve the problem of crop watering in non-rainfed or low rainfed areas. Water is required by the plants to facilitate the upward movement of nutrients. Water around the plants also lowers the temperature in the area. Some irrigation systems for agricultural practices are drip, furrow, flood, gravity, sprinkler, sub-irrigation and center-pivot irrigation.
 Problems faced by the farmers
Problems faced by the farmers
- Potential problems faced by farmers in India are:
- Very small and fragmented land holdings.
- No assurance of seed quality.
- Too much of fertilizer use depletes the soil and leads to lower yield every subsequent year.
- Availability of irrigation facilities is not adequate.
- Too much of soil erosion.
- Marketing of produce receives less attention.
- Since agriculture needs large capital investment, it is difficult for the farmers to invest much capital without the support of funding agencies.
 Modern techniques of farming
Modern techniques of farming
Modern farming techniques were deployed with two important goals in mind:
- One is to obtain higher yield and
- Second to gain more economic profit.
Six basic practices of agriculture are being developed through modern techniques, they are:
- Intensive tillage
- Mono-culture
- Use of synthetic fertilizer
- Improving irrigation technologies
- Chemical pest control
- Genetic manipulation
 Advantages of modern farming methods
Advantages of modern farming methods
Some advantages of modern farming methods are:
- Increased production
- Enhanced productivity
- Improves the socioeconomic status of farmers
- Contributes to the economy of the country
- High quality of produce
- Improved storage and reduced wastage of grains
- Protecting the crops from damage of all sorts
 Green revolution
Green revolution
Green revolution refers to the increased production of food grains by the use of high yielding varieties of seeds and better management practices. The major crops that are considered for green revolution are rice and wheat.
 Farm equipment and machinery
Farm equipment and machinery
The most commonly used machinery for the farm are
- Tractors
- Balers
- Fertilizer
- Spreader
- Seeders
- Combines
- Plows
- Mowers
- Planters
- Sprayers
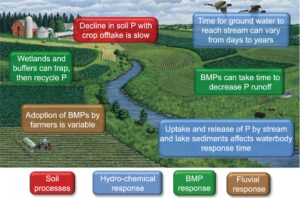 Best management practices in agriculture
Best management practices in agriculture
Management practices help farmers conserve water and enhance production. Some typical practices include:
Proper nutrient management to reduce impact on water resources.
Improved irrigation by the use of the best systems to reduce wastage of water
Protection of water resources by using buffers.
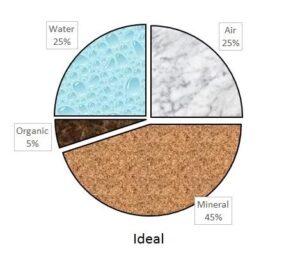 Most suitable soil for agriculture
Most suitable soil for agriculture
All over the country, different types of soil could be found and each type has unique physical, chemical and biological characteristics. Alluvial soil is considered as the most fertile soil containing potassium in it and is suitable for agricultural crops like sugarcane, paddy and plantain. Red soil has high iron content and is used for gram, groundnut and castor seed cultivation. Black soil has high calcium, magnesium and potassium used of chilly, jowar, cotton, oilseed and maize cultivation. Finally, sandy soil has low nutrient content, but is useful in growing crops like coconut.
Financial and Business expert having 30+ Years of vast experience in running successful businesses and managing finance.







