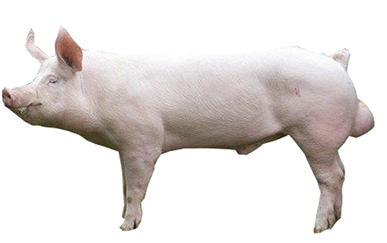
General Information
It is a small-sized animal. It is the most common breed of pig used in India. It is known for its heavy milk production and low-fat content meat production. The body is white having black pigmented spots on the body. They have longer legs, moderately long heads, slightly dished faces, pricked ears and light and long shoulders. The weight of the mature bow is 300-400kg and the mature sow is 230-320kg. It is used mainly for cross-breeding. It has a hardy nature which gets well adapted to different climatic conditions.
Fodder
Feeding management:
Pigs need feed that is nutritious as well as satisfies their hunger. Pigs love to eat fresh food. They enjoy a variety of food with having variety of textures and tastes. They will eat a wide variety of food such as water plants, fruit, nuts, meat, bush and all kinds of vegetables, especially cabbage. They also love to eat soil for the taste and texture. They will even eat happily all the unfinished food and scrap. Pigs eat an average of 2-3kg of food per day. Diet will vary on the age and weight of the pig. The pig diet must include grains and protein supplements. Mainly the healthy diets of pigs that fulfil their requirements include a mixture of cassava, sorghum, oat, wheat, rice, cotton seed cake, fish meal, meat meal, maize bran, pre-mixed vitamins and water. Vitamin B12 as a supplement is necessary in the pig diet. Mineral supplements should also be given for good growth.
Feeding of boars:
Depending upon boar age and condition feed is given accordingly. A normal boar requires 2-2.5kg concentrate/100kg weight. If pigs are kept indoors, then green feed must be given to them.
Feeding of female pigs:
Vitamins, minerals and protein content must be given in the diet. During pregnancy, the feed must be increased 1-2 before mating. A sow requires 2.5-3kg concentrate/100kg weight.
Feeding of weaner piglets:
A nourishing diet which is called as creep feed must be given to piglets. 10kg creep feed is given to each piglet before reaching the age of 8 weeks.
Care of the breed
Living requirement: For pig farming suitable land which is free from noise and is calm should be selected. All the facilities and environment which is necessary for pig farming must be there on selected land. Ensure that nearby markets and veterinary services are there. Choose a land which has a good ventilation system, suitable weather and all the necessary facilities.
Care of pregnant sow: Breeding is mainly done when male and female pigs are 8 months old. After breeding, the gestation period remains for an average of 115 days and they give birth to 8-12 piglets. Special attention is required to the pregnant sow. Separate areas, feed and water should be given to pregnant sows one week before farrowing.
Care of newborn piglets: After farrowing piglets are kept in a warm place. The mucous of each piglet must be cleaned with a soft cloth. After cleaning, the navel cord should be removed and the stumps should be cleaned with iodine. Clipping of 4 pairs of sharp teeth should be done as they help to prevent injury to teats or udder. Dry feed must be given to piglets at 2-3 weeks.
Recommended vaccines: For pigs’ good health, proper vaccines at proper times should be given. Updated vaccines as well as de-living every time are required to maintain good health. Some vaccines such as deworming are required once every year. Some major vaccines or medicines that are required for maintaining a pig’s good health are as follows:
• 3 and 10 days after the birth of the piglet, iron injection @1ml and 2ml respectively is given on the neck muscle.
• Within 24 hours of birth oral iron paste which contains iron is put in the mouth of a piglet.
• Vaccinate the pig when they are 2-4 weeks old to prevent from swine.
• Wood ash is also given as it gives important minerals to the animal.
• Feed compost of good quality is given daily for good health.
• If any symptoms are seen related to any diseases then immediately consult the vet.
Diseases and Treatment
• Colibacillosis: Firstly diarrhea occurs and then the sudden death of the animal.
Treatment: Fluid therapy or antibiotics are given to the animal to cure this disease.
• Coccidiosis: The diarrhea occurs in the 10-21 days old infancy.
Treatment: Fluid therapy or coccidiostats is given to cure the disease.
• Starvation (hypoglycaemia): Firstly the weakness occurs and then the death of the animal.
Treatment: Dextrose solutions or supplementary feeding is given to cure the disease.
• Exudative epidermitis: The skin lesions occur on the body which results in death.
Treatment: Antibiotics such as skin protectants and vitamins are given to get relief from disease.
• Respiratory disease: Sneezing, coughing and reduced growth are the symptoms of the disease and sometimes death occurs.
Treatment: By giving suitable antibiotics or by improving ventilation helps to cure the disease.
• Swine dysentery: In this disease, diarrhoea occurs with blood or diarrhoea or growth rate reduced and ultimately death of the animal.
Treatment: Reduced stocking density helps to control swine dysentery.
• Proliferative enteropathy: In this disease, diarrhoea occurs with blood or diarrhoea or growth rate reduced and ultimately sudden death of the animal.
Treatment: Iron or vitamin doses are given to cure proliferative enteropathy.
• Sarcoptic mange: The signs of this disease are itching, scratching, rubbing and reduced growth rate.
Treatment: Miticidal sprays or injections are given to cure the disease.
• Intestinal torsion: It results in the sudden death of the animal.
Treatment: Manipulation of diet will help to get rid of this disease.
• Internal pesticides (worms): In this disease, diarrhoea occurs or reduced growth or pneumonia occurs.
Treatment: The pesticides are given through feed or injection which helps to cure disease.
• Leptospirosis: The disease causes weak-born pigs or abortions.
Treatment: Inject streptomycin @25mg/kg to the weaner pigs to get rid of leptospirosis.
• Farrowing sickness: the signs of this disease are reduced milk production, loss of appetite and increased body temperature.
Treatment: Oxytocin or inflammatory drugs are given to the animal to cure from disease.
• Lameness: The disease results in reduced herd fertility and premature culling.
Treatment: No serious treatment is found but it can be prevented by preventing injuries.
• Vaginal discharge syndrome: The disease mainly causes the infections in reproductive tract.
Treatment: Antibiotic treatment of Boar’s prepuce is given to cure this disease.
• Bladder/kidney infection: blood-stained urine is the first symptom of this disease and then sudden death is seen.
Treatment: Antibiotic treatment of Boar’s prepuce is given to cure this disease.
• Erysipelas: The disease causes reproductive failure or abortions.
Treatment: Injection of penicillin @1ml/10kg body weight is given to cure erysipelas. Continue injections for 3-4 days until the disease gets cured.
• Gastric ulcers: The disease causes vomiting, loss of appetite, and blood in dung which results in sudden death.
Treatment: An extra dose of Vitamin E is given in the feed for 2 months to get a cure for gastric ulcers.
• PSS (Porcine stress syndrome): It is also known as malignant hyperthermia. The symptoms are sweating partly dead, tachycardia, arrhythmias and pyrexia.
Treatment: Dantrolene Sodium treatment under anaesthesia is an effective treatment.
Financial and Business expert having 30+ Years of vast experience in running successful businesses and managing finance.





