
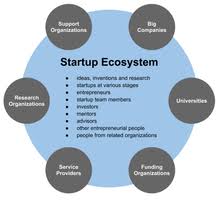
Start-up means an entity, incorporated or registered in India not prior to five years, with annual turnover not exceeding Rs.25 crore in any preceding financial year, working towards innovation, development, deployment or commercialization of new products, processes or services driven by technology or intellectual property.
- Provided that such entity is not formed by splitting up, or reconstruction, of a business already in existence.
- Provided also that an entity shall cease to be a Start-up if its turnover for the previous financial years has exceeded Rs.25 crore or it has completed 5 years from the date of incorporation/ registration.
The organizational function of the startup is to search for a repeatable and scalable business model.
A startup founder has three main functions:
- To provide a vision of a product with a set of features
- To create a series of hypotheses about all the pieces of the business model: Who are the customers? What are the distributions channels? How do we build and finance the company, etc.
- To quickly validate whether the model is correct by seeing if customers behave as your model predicts.
A startup is funded differently. While both a startup and small business will likely start with funding from the founder’s savings, friends and family, or a bank loan; if a startup is successful, it will receive additional series of funding from angel investors, venture capitalist, and eventually, an initial public offering (IPO). With each series of funding, the startup founder’s equity is windswept, while ownership of the company diversifies.
Eligibility for being a startup in India
- A recommendation (with regard to innovative nature of business), in a format specified by DIPP (Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion), from an Incubator established in a post-graduate college in India.
- An incubator, which is funded (in relation to the project) from GoI as part of any specified scheme to promote innovation
- A recommendation (with regard to innovative nature of business), in a format specified by DIPP, from an Incubator recognized by GoI.
- Be funded by an Incubation Fund/ Angel Fund/ Private Equity Fund/ Accelerator/Angel Network duly registered with SEBI that endorses innovative nature of the business.
- Be funded by GoI as part of any specified scheme to promote innovation.
- Have a patent granted by the Indian Patent and Trademark Office in areas affiliated with the nature of business being promoted.
Entity & Registrations
All businesses need one government registration or another, while nearly all require multiple registrations. For example, even air-conditioned restaurants need both service tax registration and VAT registration, depending on turnover and location, in addition to a Shops & Establishment License. Indirect taxes are those that are collected from customers by suppliers on behalf of the government. Once these taxes are paid to government, a proper record needs to be submitted periodically.
 Private Limited Company
Private Limited Company
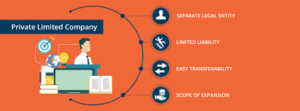
Private Limited Company, the most popular legal structure for businesses, should be chosen by anyone looking to build a scalable business. Start-ups and growing businesses choose to register a company in India because it allows outside funding to be raised easily, limits the liabilities of its shareholders and enables them to offer employee stock options to attract top talent. As these entities must hold board meetings and file annual returns with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA), they tend also to be viewed with more credibility than a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP), One Person Company (OPC), or General Partnership.
Advantages
- Limited Liability- Businesses often need to borrow money. In structures such as General Partnership, partners are personally liable for all the debt raised. So if it cannot be repaid by the business, the partners would have to sell their personal possessions to do so. In a private limited company, only the amount invested in starting the business would be Lost; the directors’ personal property would be safe.
- Investment Ready- A Private limited companies easily accommodate equity funding as there is a clear distinction between shareholders and directors as well as limited liability. In fact, venture capitalists and private equity funds are unlikely to invest in any other structure. This is because LLPs would require them to become partners in the business, while an OPC can have only one shareholder. This feature also gives you the ability to hire top talent you may not be able to afford by merely paying a salary.
- Easy Debt Access- A private limited company has more options for taking on debt than LLPs. Not only are bank loans easy to obtain (relative to OPCs and LLPs), the option of issuing debentures and convertible debentures are always available to it.
Documents required for Company Registration:
TO BE SUBMITTED BY DIRECTORS & SHAREHOLDERS
- Scanned copy of PAN Card or Passport (Foreign Nationals & NRIs)
- Scanned copy of Voter’s ID/Passport/Driver’s License/Aadhar
- Scanned copy of Latest Bank Statement/Telephone or Mobile, Electricity or Gas Bill
- Scanned passport-sized photograph
- Specimen signature (blank document with signature [directors only])
FOR THE REGISTERED OFFICE
- Scanned copy of Latest Bank Statement/Telephone or Mobile, Electricity or Gas Bill
- Scanned copy of Notarized Rental Agreement in English
- Scanned copy of No-objection Certificate from property owner
- Scanned copy of Sale Deed/Property Deed in English (in case of owned property)
 Public Limited Company
Public Limited Company
Public Limited Company is a company whose shares are traded in stock market or issues fixed deposits. For Public Limited Company Registration, the company must have minimum 3 Directors, 7 Shareholders and Maximum 50 Directors and need Rs.5 Lakhs of Paid up Capital. A Public limited company have all the advantages of Private Limited Company and the ability to have any number of members, ease in transfer of shareholding and more transparency.
Documents required for Company Registration
TO BE SUBMITTED BY DIRECTORS & SHAREHOLDERS
- Scanned copy of PAN Card or Passport (Foreign Nationals & NRIs)
- Scanned copy of Voter’s ID/Passport/Driver’s License/Aadhar
- Scanned copy of Latest Bank Statement/Telephone or Mobile, Electricity or Gas Bill
- Scanned passport-sized photograph
- Specimen signature (blank document with signature [directors only])
FOR THE REGISTERED OFFICE
- Scanned copy of Latest Bank Statement/Telephone or Mobile, Electricity or Gas Bill
- Scanned copy of Notarized Rental Agreement in English
- Scanned copy of No-objection Certificate from property owner
- Scanned copy of Sale Deed/Property Deed in English (in case of owned property)
 One Person Company
One Person Company
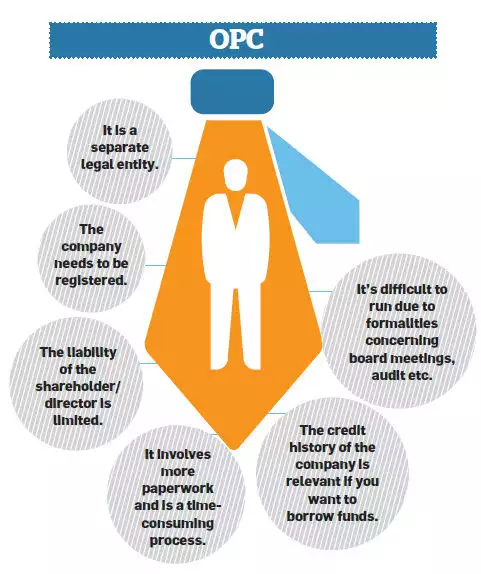
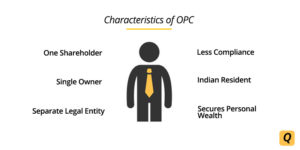
The One Person Company (OPC) was recently introduced as a strong improvement over the sole Proprietorship. It gives a single promoter full control over the company while limiting his/her liability to contributions to the business. This person will be the only director and shareholder (there is a nominee director, but with no power until the original director is incapable of entering into contract). So there’s no chance of rising equity funding or offering employee stock options. Furthermore, if an OPC hits an average three-year turnover of over Rs. 2 crore or has a paid-up capital of over Rs.50 lakh, it must be turned into a private limited company or public limited company within six months.
Advantage
- Continuous Existence– Sole Proprietorship come to an end with the death of the proprietor. As an OPC has a separate legal identity, it would pass on to the nominee director and, therefore, continue to exist.
- Greater Credibility- As an OPC needs to have its books audited annually, it has greater credibility among vendors and lending institutions.
Documents Required for Registration
TO BE SUBMITTED BY PARTNERS
- Scanned copy of PAN Card or Passport
- Scanned copy of Voter’s ID/Passport/Driver’s License/Aadhar
- Scanned copy of Latest Bank Statement/Telephone or Mobile, Electricity or Gas Bill
- Scanned passport-sized photograph
- Specimen signature blank document with signature
FOR THE REGISTERED OFFICE
- Scanned copy of Latest Bank Statement/Telephone or Mobile, Electricity or Gas Bill
- Scanned copy of Notarized Rental Agreement in English
- Scanned copy of No-objection Certificate from property owner
- Scanned copy of Sale Deed/Property Deed in English (in case of owned property)
 Partnership Firm
Partnership Firm
Advantages
- Minimal Compliance- General Partnerships do not need to appoint an auditor or, if unregistered, even file annual accounts with the registrar Annual compliance are also fewer as compared to an LLP.
- Easy to start- It can be started with just an unregistered Partnership Deed in 2 to 4 days; registration, however, does bring a few advantages. It would enable you to file suits in court against another firm or partners in the firm for the enforcement of rights arising from a contract or right given by the Partnership Act.
- Relatively Inexpensive- A General Partnership is cheaper to start than an LLP and even over the long-term, thanks to the minimal compliance requirements, is inexpensive. You would not need to hire an auditor, for example. This is why, despite its severe shortcoming (unlimited liability), home businesses may opt for it.
Documents required for Registration
- Form No. 1 (Application for registration under Partnership Act)
- Original copy of Partnership Deed, signed by all partners
- Affidavit declaring intention to become partner
- Rental or lease agreement of the property/campus on which the business is set
 Sole Proprietorship Firm
Sole Proprietorship Firm
Advantages
- Minimal Compliance- Sole Proprietorship are only recognized via their government and tax registrations, so the extent of their compliance is limited to the annual filing of their service, professional or sales taxes.
- Easy to start- A sole proprietorship could take only 3-4 days to start because all you need is a GST registration. Either way, the process is uncomplicated. PAN card and identity and address proofs are enough to get them done.
- Relatively Inexpensive- A Sole Proprietorship is inexpensive as compared to a One-person Company (OPC) and, thanks to the minimal compliance requirements, is inexpensive even over the long-term. You would not need to hire an auditor, for example. This is why, despite its severe shortcoming (unlimited liability), small merchants and traders opt for it.
 Limited Liability Partnership
Limited Liability Partnership
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP), introduced only in 2008, has quickly become a popular legal structure for businesses. Its main improvement over the General Partnership is that, as the name indicates, it limits the liabilities of its partners to their contributions to the business and also offers each partner protection from the negligence, misdeeds or incompetence of the other partners.
- Limited Liability- Businesses often need to borrow money. In a General Partnership, partners are personally liable for all this debt. So if it cannot be repaid by the business, the partners would have to sell their personal possessions to do so. In an LLP, only the amount invested in starting the business would be lost; all personal property would be safe.
- Reduced Compliance- An LLP only requires audited annual returns to be filed if it has a turnover of greater than Rs.40 lakhs or capital contribution of over Rs.25 lakhs. It also needs to communicate fewer business transactions and structural changes than a private limited company.
- Tax Advantages- There are some important advantages over the private limited company. For example, Dividend Distribution Tax and tax surcharge don’t apply. Loans to partners are also not taxable as income.
Documents Required for LLP Registration
TO BE SUBMITTED BY PARTNERS
- Scanned copy of PAN Card or Passport (Foreign Nationals & NRIs)
- Scanned copy of Voter’s ID/Passport/Driver’s License/Aadhar
- Scanned copy of Latest Bank Statement/Telephone or Mobile, Electricity or Gas Bill
- Scanned passport-sized photograph
- Specimen signature (blank document with signature [directors only])
FOR THE REGISTERED OFFICE
- Scanned copy of Latest Bank Statement/Telephone or Mobile, Electricity or Gas Bill
- Scanned copy of Notarized Rental Agreement in English
- Scanned copy of No-objection Certificate from property owner
- Scanned copy of Sale Deed/Property Deed in English (in case of owned property)
Important Links:
https://www.startupindia.gov.in/content/sih/en/startup-scheme.html
Financial and Business expert having 30+ Years of vast experience in running successful businesses and managing finance.





